Tropomyosin is a long, thin protein that helps regulate the interaction between actin and myosin filaments. It lies along the actin filaments and blocks the binding sites for myosin. When a nerve impulse triggers a muscle contraction, a molecule called calcium ions is released into the muscle cell. This causes troponin to bind to actin and move.. Action potentials in the motor neuron result in the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter, at the neuromuscular junction. Acetylcholine binds to receptors on the muscle cell membrane, triggering an action potential in the muscle cell. This leads to the release of calcium ions into the cytoplasm, starting the process of muscle contraction.

Muscle Contraction Process Molecular Mechanism [3D Animation] (+playlist) Teaching biology

Muscle Contraction Cycle Muscular system anatomy, Basic anatomy and physiology, Muscle contraction
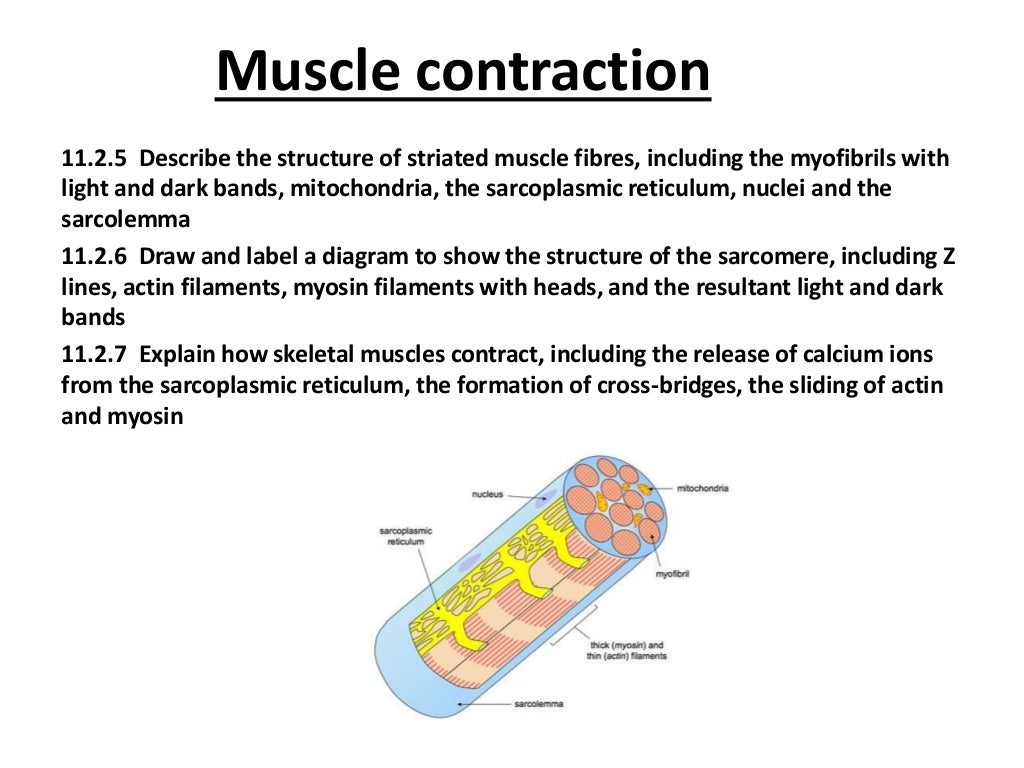
Muscle contraction Higher Level Biology IB
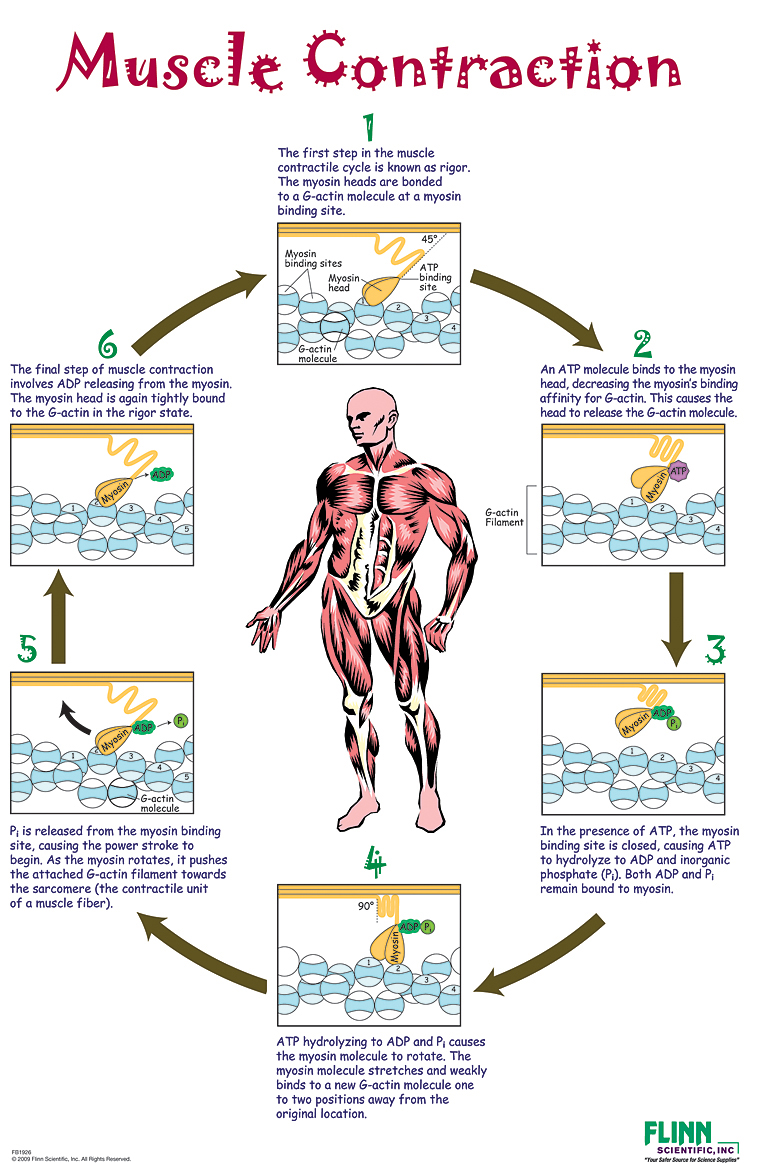
Muscle Contraction Poster Flinn Scientific

Musclular System Labeled Back Human Muscle System Functions Diagram Facts Britannica xaqukao7

6.3 Muscle Contraction Introductory Animal Physiology 2nd Edition

FREE GCSE A Level Biology Muscle Contraction Practice Exam Question Teaching Resources

Sliding Filament Model of Contraction Biology for Majors II
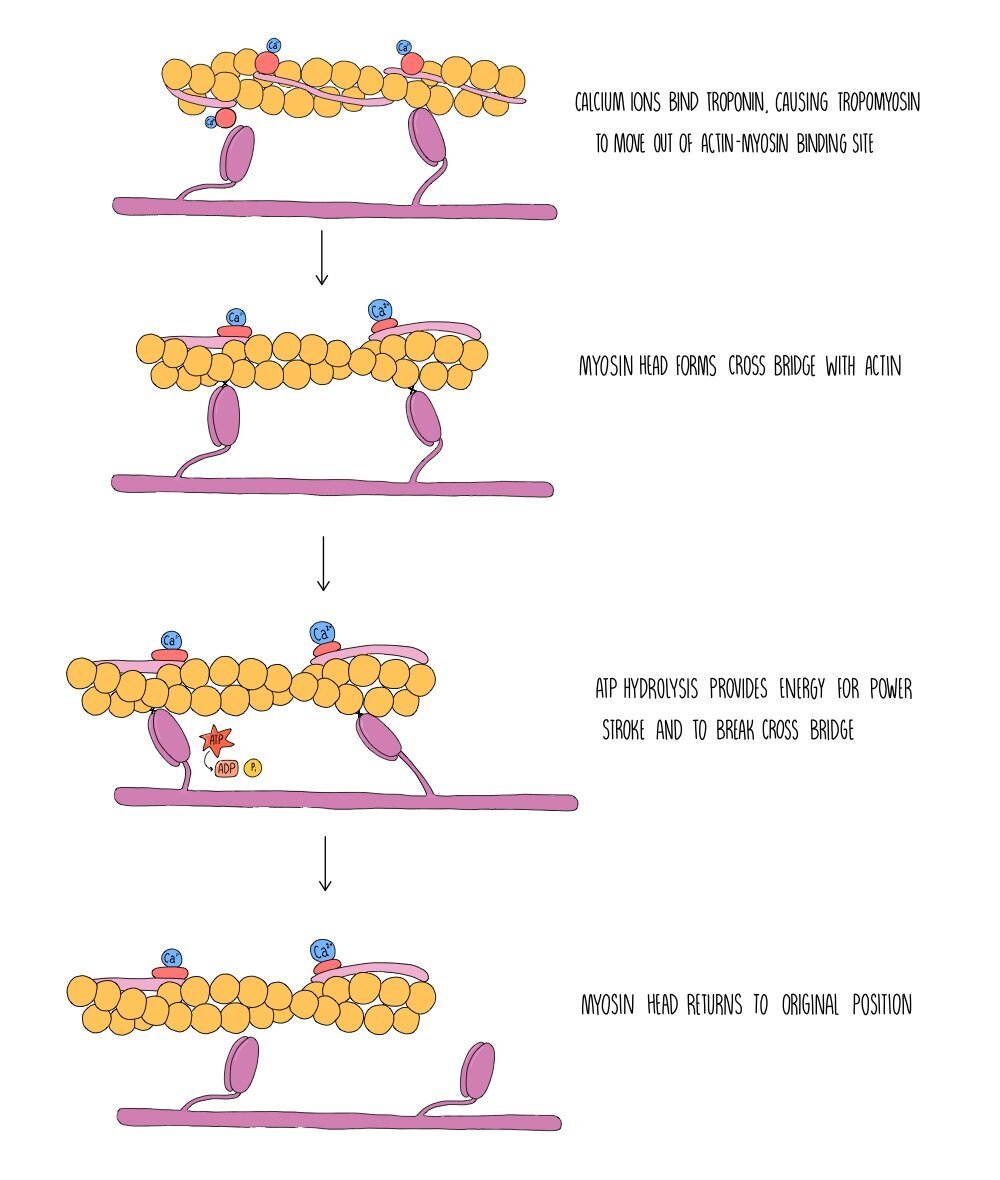
Muscle Contraction AQA — the science hive

thefatstudent “932pm// Sliding Filament Theory of muscle contraction poster to go on my

Flashcards Revision, Gcse Biology Revision, A Level Biology, Muscle Contraction, Contractions

Full Science Lessons by Theresa Teaching Resources TES
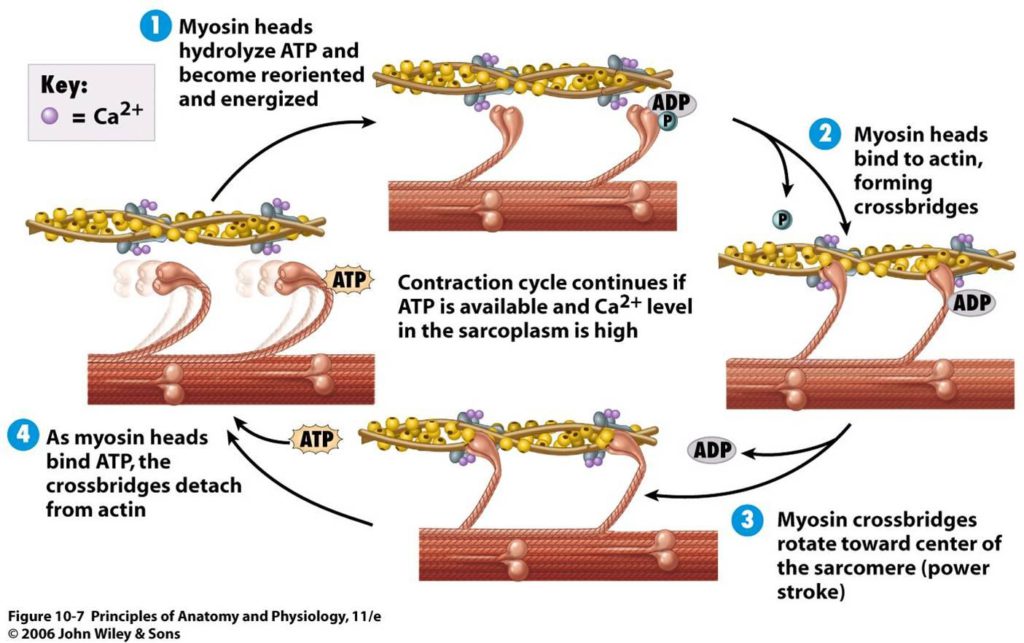
Forensic science Archives Christie’s Mysteries

Image result for muscle cell Exercise Physiology, Anatomy And Physiology, Muscular System

muscle contraction Biology Notes, Science Notes, Cell Biology, Molecular Biology, Science

A2 Biology Muscle Contraction Teaching Resources Biology worksheet, Flashcards revision, Biology

Muscle contraction Higher Level Biology IB

Explain the mechanism of muscle contraction with a diagram.
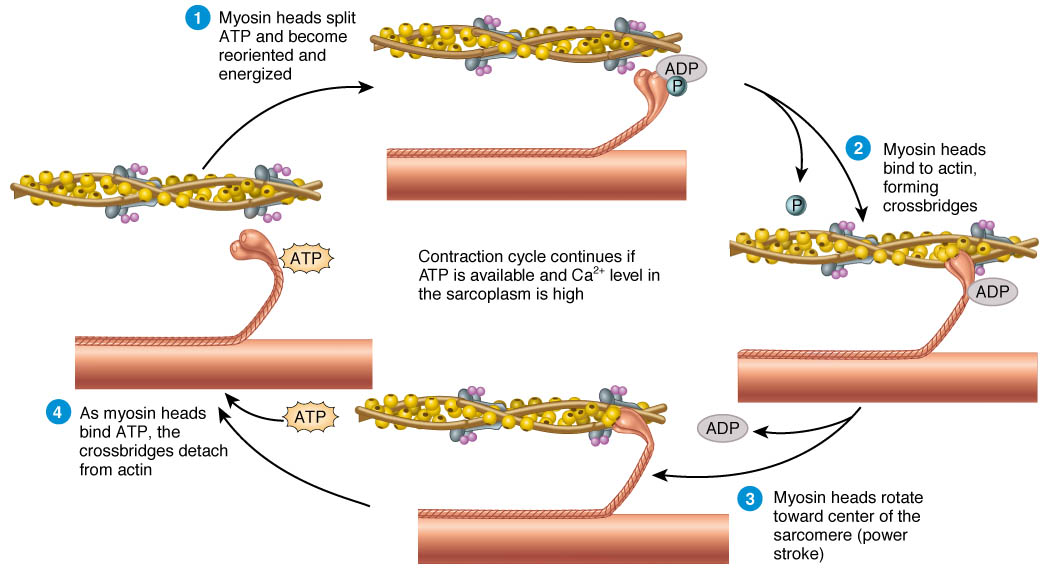
A Basic Look At How A Muscle Contracts

Explain the mechanism of muscle contraction with a diagram.
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 9, s6-s7 (2008) doi:10.1038/nrm2581. Goody, R. S. The missing link in the muscle cross-bridge cycle. Nature Structural Molecular Biology 10, 773-775 (2003.. How muscles contract – the sliding filament model. Muscles cause movement by contracting; During muscle contraction, sarcomeres within myofibrils shorten as the Z discs are pulled closer together This is known as the sliding filament model of muscle contraction and occurs via the following process:. An action potential arrives at the neuromuscular junction